Clinical Trials

Stress Reduction in Perioperative Care: Feasibility Randomized Controlled Trial
Patients undergoing surgery often experience stress and anxiety, which can increase complications and hinder recovery. Effective management of these psychological factors is key to improving outcomes.
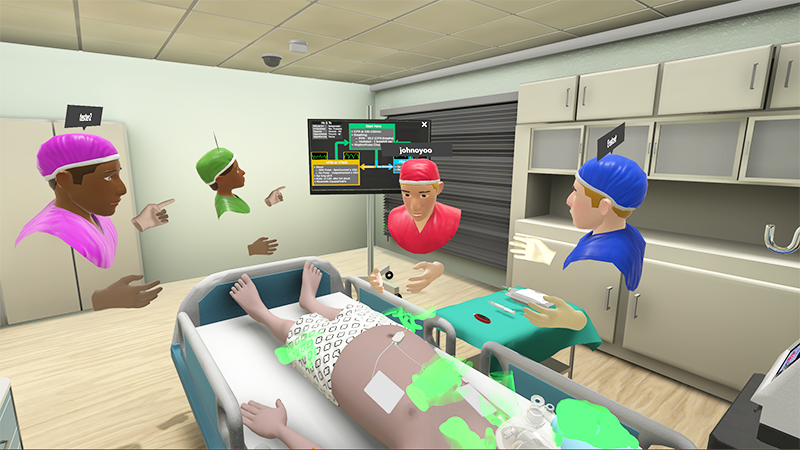
Elucidating cognitive processes in cardiac arrest team leaders: a virtual reality-based cued-recall study of experts and novices
Team leadership during medical emergencies like cardiac arrest resuscitation is cognitively demanding, especially for trainees. These cognitive processes remain poorly characterized due to measurement challenges. Using virtual reality simulation, this study aimed to elucidate and compare communication and cognitive processes-such as decision-making, cognitive load, perceived pitfalls, and strategies-between expert and novice code team leaders to inform strategies for accelerating proficiency development.
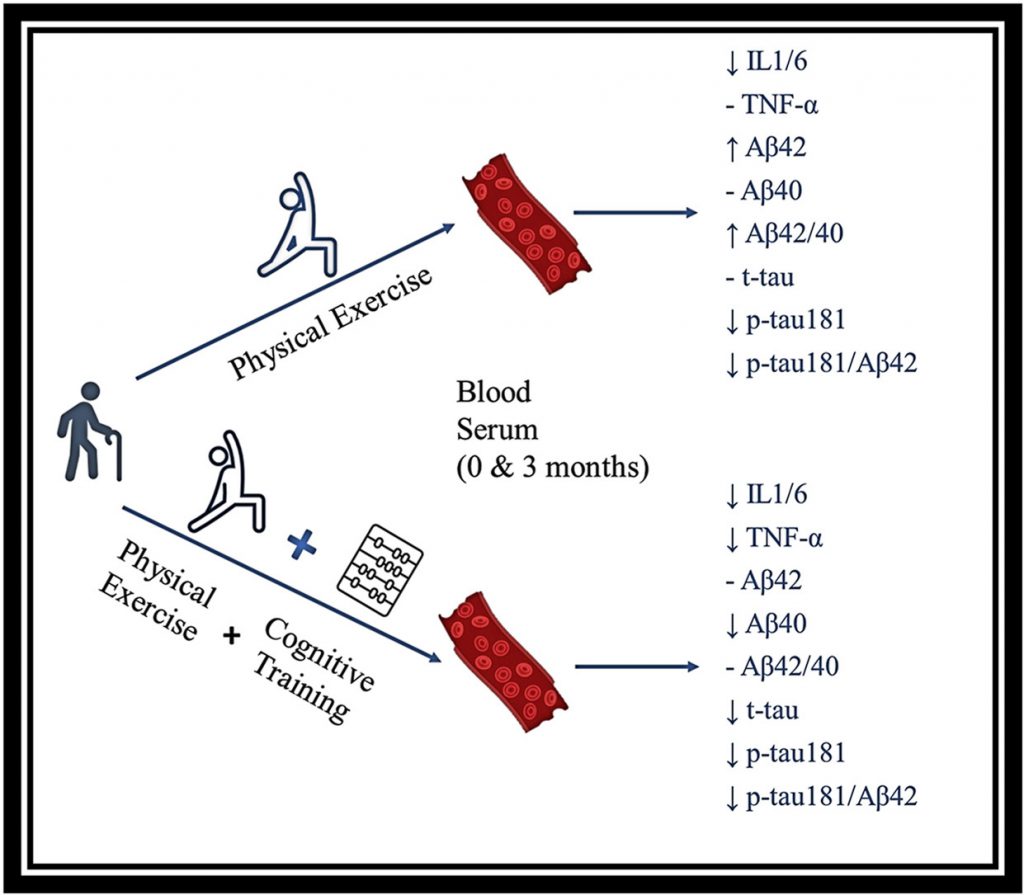
The effect of physical exercise with cognitive training on inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers of Mild Cognitive Impairment patients
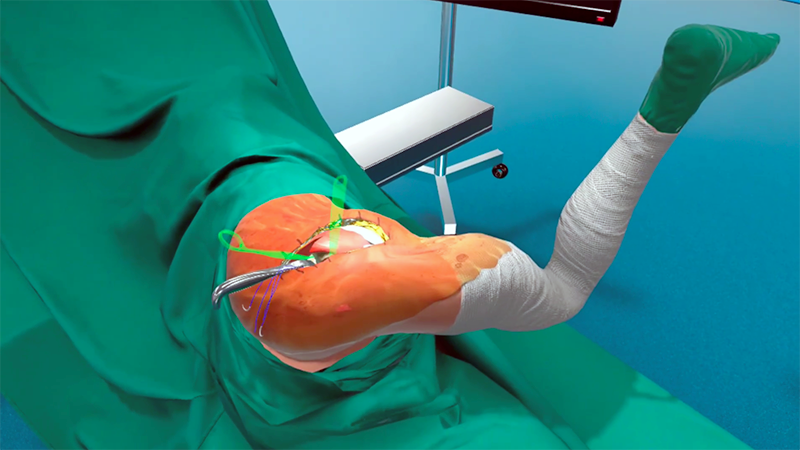
Effectiveness of virtual reality compared to video training on acetabular cup and femoral stem implantation accuracy in total hip arthroplasty among medical students: a randomised controlled trial
Virtual reality (VR) training effectiveness in improving hip arthroplasty surgical skills requires further evaluation. We hypothesised VR training could improve accuracy and the time taken by medical students compared to a control group with only video teaching.
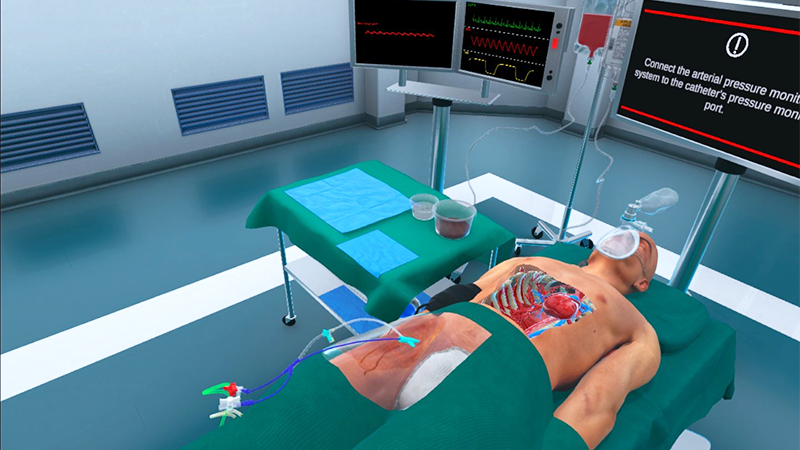
Development and usability testing of a fully immersive VR simulation for REBOA training
Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) is a potentially life-saving procedure for bleeding trauma patients. Being a rare and complex procedure performed in extreme situations, repetitive train- ing of REBOA teams is critical. Evidence-based guidelines on how to train REBOA are missing, although simulation- based training has been shown to be effective but can be costly and complex.

VRADA training system as a non-pharmacological dual intervention to alleviate symptoms of the pathophysiology of Mild Cognitive Impairment
In this study, a VR system called VRADA (VR Exercise App for Dementia and Alzheimer’s Patients) was designed for physical and cognitive training forindividuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). The inflammatory factors IL-1β and TNF-α, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) hallmarks total tau, p181-tau, Αβ42 and Aβ40, the ratio of Aβ42/40 and p181-tau/Aβ42 were assessed on the blood serum of patients diagnosed with MCI to determine the effect of VRADA training.

Training for Better Transfer in an Online Competency-Based Higher Education Program: Technology’s Role in Preparing the Next Generation Workforce
Virtual reality simulations represent a much-needed effort to move beyond the shortcomings of traditional form-based assessments. Within VR, we assess competency and problem-solving skills versus the content memorization typically supported by conventional measures. This chapter explores an innovative VR simulation recently deployed at Western Governors University.
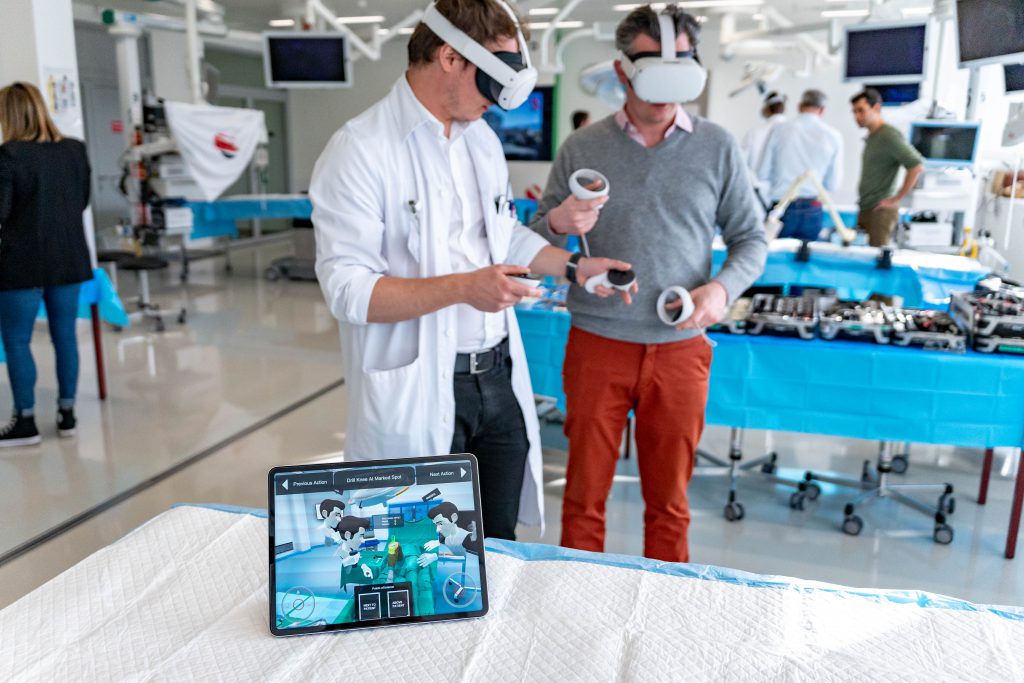

Virtual Reality Simulation Facilitates Resident Training in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial
No study has yet assessed the efficacy of virtual reality (VR) simulation for teaching or- thopedic surgery residents. In this blinded, randomized, and controlled trial, we asked if the use of VR simulation improved postgraduate year (PGY)-1 orthopedic residents’ performance in cadaver total hip arthroplasty and if the use of VR simulation had a preferentially beneficial effect on specific aspects of surgical skills or knowledge.

Virtual Reality Medical Training for COVID-19 Swab Testing and Proper Handling of Personal Protective Equipment: Development and Usability
Efficient and riskless training of healthcare professionals is imperative as the battle against the Covid-19 pandemic still rages. Recent advances in the field of Virtual Reality (VR), both in software and hardware level, unlocked the true potential of VR medical education. The main objective of this work is to describe the algorithms, models and architecture of a medical virtual reality simulation aiming to train medical personnel and volunteers in properly performing Covid- 19 swab testing and using protective measures, based on a world-standard hygiene protocol.

A Digital Health Intervention for Stress and Anxiety Relief in Perioperative Care: Protocol for a Feasibility Randomized Controlled Trial
This study aimed to explore the feasibility of a digital health intervention called the Adhera CARINAE Digital Health Program, designed to provide evidence-based, personalized stress- and anxiety-management methods enabled by a comprehensive digital ecosystem that incorporates wearable, mobile, and virtual reality technologies. The intervention program includes the use of advanced data-driven techniques for tailored patient education and lifestyle support.

Α Virtual Reality App for Physical and Cognitive Training of Older People With Mild Cognitive Impairment: Mixed Methods Feasibility Study
Therapeutic virtual reality (VR) has emerged as an effective treatment modality for cognitive and physical training in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). However, to replace existing nonpharmaceutical treatment training protocols, VR platforms need significant improvement if they are to appeal to older people with symptoms of cognitive decline and meet their specific needs

Effectiveness and Utility of Virtual Reality Simulation as an Educational Tool for Safe Performance of COVID-19 Diagnostics: Prospective, Randomized Pilot Trial
Although the proper use of hygiene and personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount for preventing the spread of diseases such as COVID-19, health care personnel have been shown to use incorrect techniques for donning/doffing of PPE and hand hygiene, leading to a large number of infections among health professionals. Education and training are difficult owing to the social distancing restrictions in place, shortages of PPE and testing material, and lack of evidence on optimal training. Virtual reality (VR) simulation can offer a multisensory, 3-D, fully immersive, and safe training opportunity that addresses these obstacles.
Case Studies

University of Michigan - Medicine
Advancing Healthcare Excellence Through Education and Innovation
Advanced approaches for comprehensive analysis and enhancement of cardiac arrest resuscitation training for emergency medicine and nursing. Read More
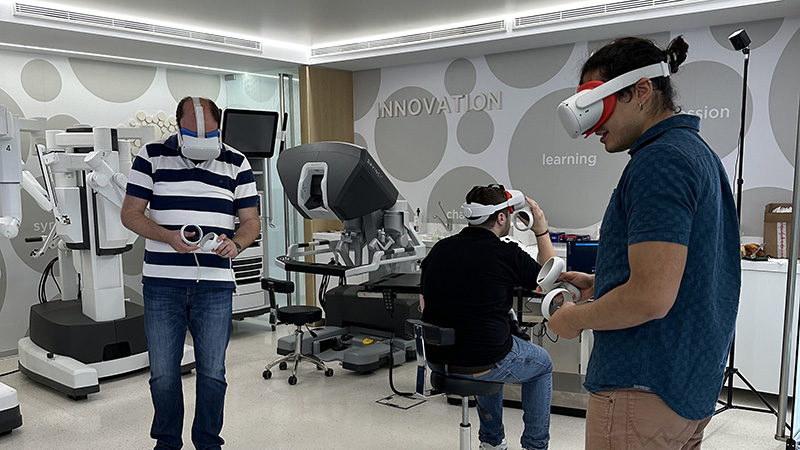

Sofmedica
Pioneering Excellence in Medical Education and Innovation
Train anywhere, any time. Minimal equipment required for simulating the whole robotic experience. Read More
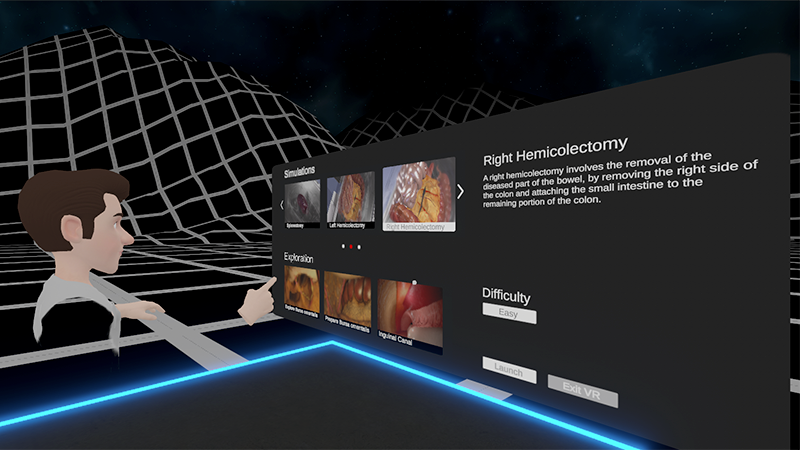
University Hospital Cologne
One of Germany’s most outstanding medical centers
Largest ever interactive abdominal anatomy and surgery collection of XR simulations. An In-Depth First-Person Exploration of Topographical Anatomy from the Inside Out. Read More

Insespital - Universitätsspital Bern
One of the six hospitals of the Insel Group – Switzerland’s leading full-service medical care system.
COVID-19 XR Simulation: Nasopharyngeal Swab, Hand Hygiene & Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Read More
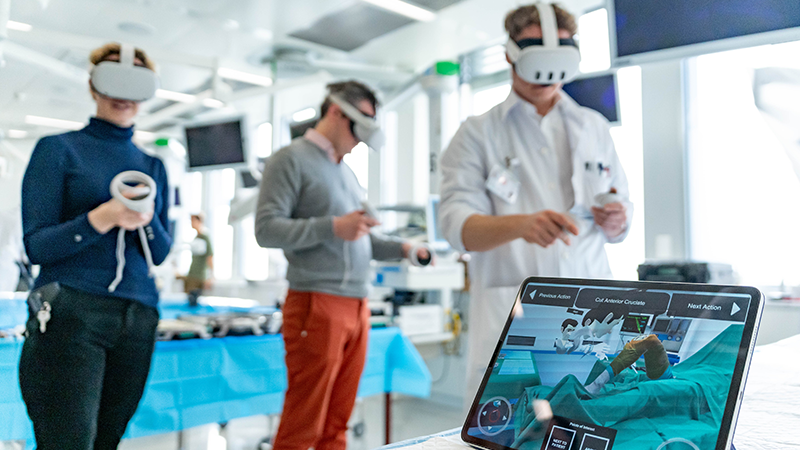

NYU Langone Health
One of the largest Healthcare systems in the Northeast
First-ever collaborative VR surgical training, connecting 4 reputable Medical schools. Read More
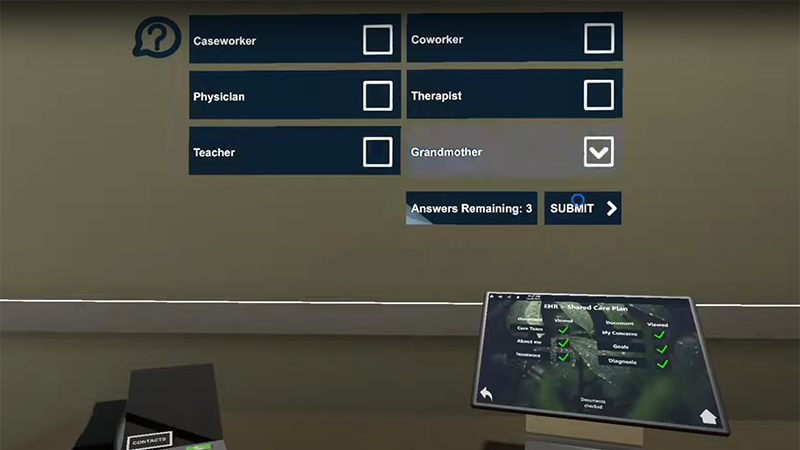
Western Governors University
Transforming Higher Education Through Competency-Based Learning
Cognitive training and assessment simulations for soft skills. Skill-based scoring system for a collaborative environment. Read More

Centre for Virtual Medicine, Geneva University Hospitals
The first Hospital-based Department of Virtual Medicine
MAGES SDK: Empowering Extended Reality OSCE Development. Read More
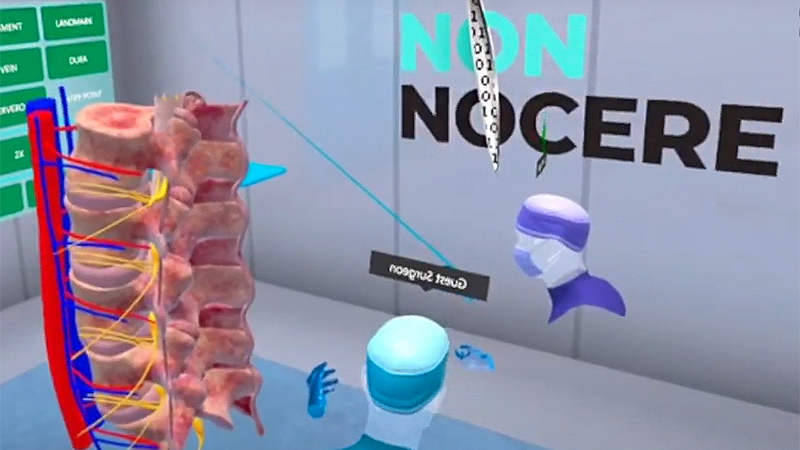
Non Nocere
Medical Virtual Reality Training Provider
Patient specific Data Visualization and Surgical planning. Acclaimed by Spine Surgeons and used in various specialties and simulation training courses. Read More

“MAGES SDK allowed us to create VR content with minimal effort!
Dr. Stefan Tuchschmid,
CO-CEO & Founder, VirtaMed AG

“Thanks to its high-quality toolset and capabilities, the MAGES SDK has allowed us to create and author simulations in a very time and resource efficient manner!”
Josh Tan,
Diagnostic Radiology, Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, USA

“MAGES SDK has streamlined our pipeline incredibly. The development and feedback loop has been so tight that in about one month we had a full – blown teaching tool!”
Sinan Vural,
CTO, Non Nocere, Germany

“We have worked with ORamaVR and our residents absolutely love training with the platform. This has really been good for our training, we are really encouraged with this technology and I am really trying to interest all my colleagues and training centers that this is neccessary for them to make their residents better.”
Prof. Lawrence Dorr,
Orthopaedics University of Southern California, Keck School of Medicine, USA

Prof. Per Kjaersgaard-Andersen and
Colleagues,
South Danish University, Denmark

“VR is the future of medical education and we are pushing further the limits with ORamaVR and MAGES SDK”
Prof. Thomas Sauter,
Emergency Telemedine, University of Bern, Switzerland

“Very nice experience and it will be very fruitfull for young surgeons. It’s a great tool and helpful for the
training.“
Lazaros A. Poultsides,
MD, MSc, PhD. NYU Langone Medical Associate

Prof Paul K. Gilbert,
Orthopaedics University of Southern California, Keck School of Medicine, USA
